Locks have been an integral part of human society for millennia, safeguarding our most precious possessions and spaces. Among the myriad lock designs that have emerged throughout history, the Yale lock stands out as a revolutionary invention that has shaped modern security systems. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of lock mechanisms, with a particular focus on the innovative Yale lock and its profound impact on security technology.
The Foundations of Lock Design
Before exploring the specifics of Yale locks, it's crucial to understand the fundamental principles behind lock mechanisms. At its core, a lock is a mechanical or electronic device designed to secure an object or space, preventing unauthorized access. While the concept may seem simple, the execution can be remarkably complex.
Key Components of a Basic Lock
The anatomy of a basic lock includes several essential components:
- The bolt: A movable bar that extends into the door frame, securing the door when in the locked position.
- The cylinder: The part of the lock where the key is inserted.
- Pins: Small metal components inside the cylinder that must be aligned correctly for the lock to open.
- Springs: Provide tension to keep the pins in place.
- The key: The external device used to operate the lock.
These components work in harmony to create a secure barrier against unauthorized entry. However, it wasn't until the mid-19th century that lock design underwent a revolutionary change with the advent of the Yale lock.
The Birth of the Yale Lock: A Paradigm Shift in Security
The Yale lock, as we know it today, is the brainchild of Linus Yale Jr., who revolutionized lock design in the 1860s. However, the story of Yale locks begins much earlier with his father, Linus Yale Sr.
Linus Yale Sr.: Laying the Groundwork
Linus Yale Sr. began experimenting with lock designs in the 1840s, focusing primarily on improving bank locks and safe locks. His work laid the crucial foundation for what would eventually become the Yale company. Yale Sr.'s contributions to lock technology were significant, but it was his son who would truly revolutionize the industry.
Linus Yale Jr.'s Breakthrough: The Modern Pin Tumbler Lock
Building upon his father's work, Linus Yale Jr. took lock design to the next level. In 1861, he patented a small, flat key with serrated edges, which we now recognize as the modern pin tumbler lock. This design was a significant improvement over the large, heavy keys of the time and would go on to change the face of security forever.
Yale Jr.'s innovation wasn't just about the key, though. The real genius lay in the lock mechanism itself. The pin tumbler system he developed was elegant in its simplicity yet highly effective in its function. This new design offered improved security, ease of use, and the potential for mass production – a combination that would prove irresistible to both consumers and manufacturers.
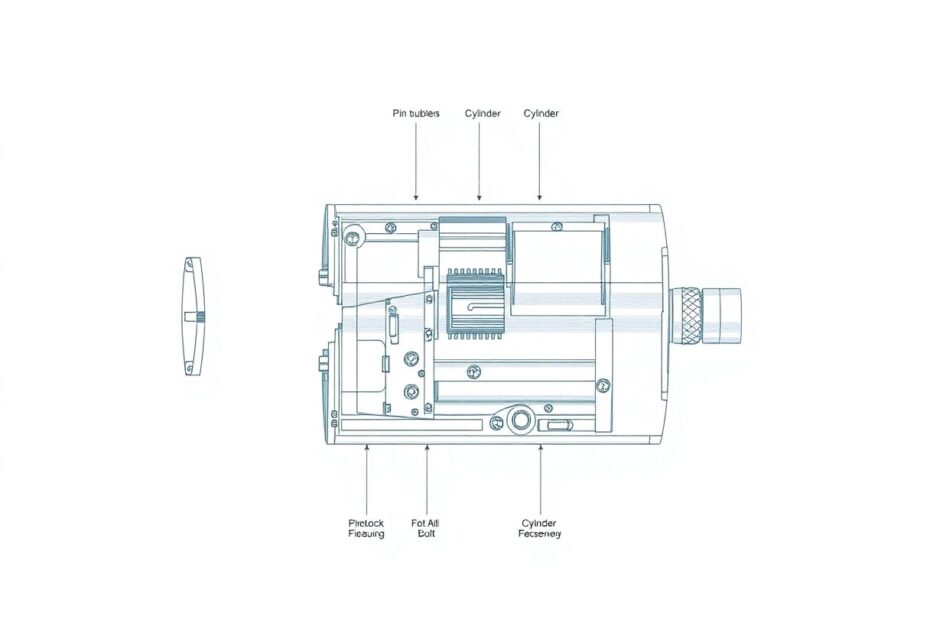
The Mechanics of Yale Locks: Understanding the Pin Tumbler System
The brilliance of the Yale lock lies in its ingenious pin tumbler mechanism. Let's break down how it operates:
The lock consists of a cylinder that rotates within the lock body.
Inside the cylinder are several pin stacks, typically 5 or 6. Each stack consists of two parts:
- Key pins: The lower pins that come into direct contact with the key.
- Driver pins: The upper pins pushed down by springs.
The shear line is the gap between the cylinder and the lock body.
When you insert the correct key, its grooves push the key pins up to precisely the right height.
If the key is correct, it will push the meeting point between the key pins and driver pins exactly to the shear line.
With all pins aligned at the shear line, the cylinder can rotate freely, operating the bolt and opening the lock.
This mechanism's elegance lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. The pin tumbler system made locks more secure, harder to pick, and easier to mass-produce, leading to its widespread adoption.
The Impact of Yale's Design: Revolutionizing Security Standards
The introduction of Yale locks had a profound effect on security practices worldwide. Here's how Yale's innovation changed the landscape:
1. Standardization of Security
Yale's design quickly became a standard, influencing lock manufacturers across the globe. This standardization led to more consistent security measures and easier integration of locks into various systems.
2. Improved Home Security
The affordability and effectiveness of Yale locks made robust security accessible to average homeowners. For the first time, high-quality locks were not just for banks and wealthy individuals but could be found in homes across socioeconomic spectrums.
3. Business Applications
The ability to create complex master key systems revolutionized access control in businesses and institutions. Organizations could now implement hierarchical access systems, allowing different levels of access for various employees or residents.
4. Influence on Lock Picking
The pin tumbler design raised the bar for lock picking, leading to advancements in both security and lock-picking techniques. This ongoing "arms race" between locksmiths and lock pickers has driven continuous innovation in the field.
Evolution of Yale Locks: Adapting to Modern Challenges
Since its inception, the Yale lock has undergone numerous improvements to keep pace with evolving security needs:
Increased Pin Numbers
Early Yale locks had only 3 or 4 pin stacks. Modern locks often have 5, 6, or even 7, dramatically increasing the number of possible key combinations. This exponential increase in combinations makes locks significantly harder to pick or duplicate keys without authorization.
Master Key Systems
Yale developed systems allowing multiple levels of access. For instance, in an apartment building, each tenant's key works only for their apartment, while the building manager's key can open all doors. This innovation greatly simplified key management for large buildings and institutions.
High-Security Variations
To combat increasingly sophisticated lock-picking techniques, Yale and other manufacturers have introduced high-security variations of the pin tumbler lock. These include:
- Mushroom Pins: These specially shaped pins make lock picking more difficult by creating false set points.
- Sidebar Mechanisms: An additional locking element that must be engaged for the lock to open, providing an extra layer of security.
Electronic Integration
Modern Yale locks often incorporate electronic components, allowing for keyless entry through keypads or smartphone apps. These smart locks offer conveniences like remote access control and activity logging, bridging the gap between traditional mechanical security and the digital age.
Yale Locks vs. Other Mechanisms: A Comparative Analysis
While Yale locks dominate the market, it's worth comparing them to other lock types to understand their advantages and limitations:
Warded Locks
- How they work: Use a set of obstructions (wards) that the key must pass by.
- Comparison: Much simpler and less secure than Yale locks. Warded locks are easier to pick and offer fewer unique key combinations.
Wafer Tumbler Locks
- How they work: Similar to pin tumblers but use flat wafers instead of pins.
- Comparison: Generally less secure than Yale locks but used in many automobiles due to their compact size and ease of manufacture.
Disc Tumbler Locks
- How they work: Use rotating discs that must be aligned to open.
- Comparison: Can be more pick-resistant than standard pin tumbler locks, but are often more expensive and complex to manufacture.
The Future of Yale Locks: Innovations on the Horizon
As we look to the future, Yale continues to innovate, pushing the boundaries of lock technology:
1. Smart Locks
Integrating Wi-Fi and Bluetooth technology for remote access and monitoring, smart locks are becoming increasingly sophisticated. These locks can be controlled via smartphone apps, allowing users to grant temporary access, monitor entry logs, and receive alerts about unusual activity.
2. Biometric Systems
Yale is exploring the integration of biometric technology, such as fingerprint or retinal scan systems, into their locks. This technology promises to offer enhanced security and convenience, eliminating the need for physical keys altogether.
3. AI and Machine Learning
The next frontier in lock technology involves the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Yale is developing locks that can learn and adapt to user behavior patterns, potentially identifying and alerting owners to suspicious activity.
4. Sustainable Materials
In response to growing environmental concerns, Yale is exploring eco-friendly materials and production methods for their locks. This includes the use of recycled materials and the development of manufacturing processes with a lower carbon footprint.
Understanding and Maintaining Your Yale Lock
For those interested in the practical aspects of Yale locks, here are some tips for understanding and maintaining your lock:
DIY Lock Exploration
- Observe the Key: Look at the ridges on your key. Each corresponds to a pin stack in the lock.
- Feel the Pins: When you insert the key slowly, you can feel each pin stack being pushed up.
- Listen Closely: As you turn the key, listen for the slight click as the pins align and the cylinder turns.
Note: Never attempt to disassemble a lock in use, as this could damage it or void warranties.
Maintenance Tips
To ensure your Yale lock continues to function properly:
- Regular Cleaning: Use a dry lubricant spray annually to keep the mechanism smooth.
- Avoid Liquid Lubricants: These can attract dust and gum up the mechanism.
- Check for Loose Parts: Periodically ensure all visible screws are tight.
- Professional Servicing: Have a locksmith check your lock every few years, especially for high-security applications.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Yale Locks
The Yale lock, with its elegant pin tumbler design, has stood the test of time for over 150 years. Its impact on security, both in our homes and in the broader world, cannot be overstated. As we continue to face new security challenges in an increasingly digital world, the principles behind the Yale lock – simplicity, effectiveness, and adaptability – continue to inspire innovations in the field of security.
From its humble beginnings in Linus Yale Jr.'s workshop to its current status as a global security standard, the Yale lock serves as a testament to the power of ingenious design. It reminds us that sometimes, the most profound innovations come not from complexity, but from refining and perfecting simple, fundamental concepts.
As we look to the future, it's clear that while the technology around us may change dramatically, the core principles of the Yale lock will continue to play a crucial role in keeping our possessions, our homes, and our lives secure. The story of the Yale lock is not just about a mechanical device; it's about the ongoing human quest for safety and peace of mind in an ever-changing world.
In an age where digital security often takes center stage, the enduring relevance of the Yale lock reminds us of the importance of physical security. As we continue to innovate and adapt to new challenges, the legacy of Linus Yale Jr. and his revolutionary lock design will undoubtedly continue to influence and inspire security solutions for generations to come.