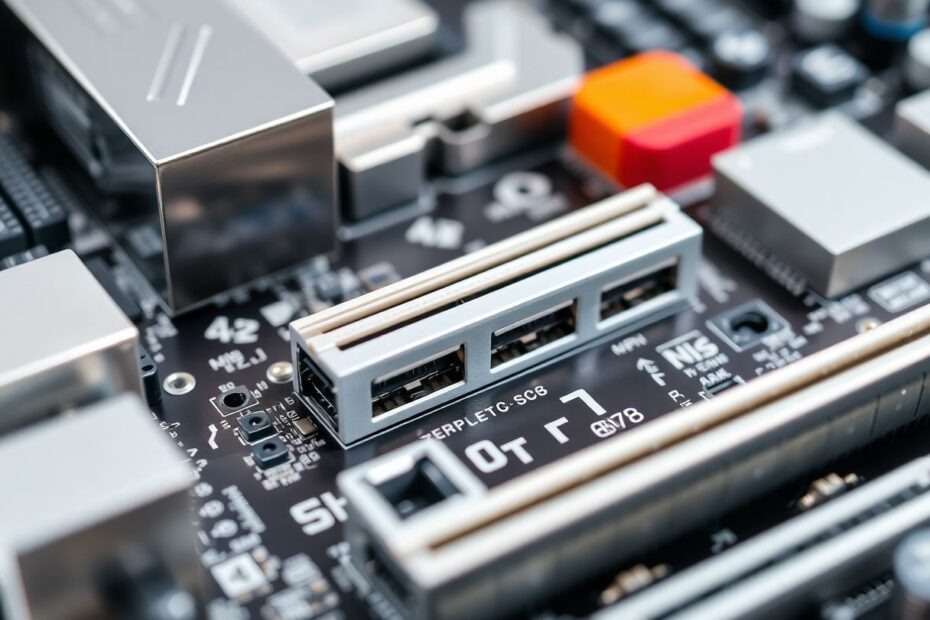
As a passionate tech enthusiast, I'm excited to take you on a deep dive into the fascinating world of motherboard connectors. Whether you're a seasoned PC builder or a curious newcomer, understanding these crucial components is key to mastering computer assembly and troubleshooting. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various connectors that bring your computer to life, delving into their functions, characteristics, and best practices for usage.
The Motherboard: The Nervous System of Your Computer
The motherboard is often referred to as the nervous system of a computer, and for good reason. It's the central hub where all components converge, facilitating communication and power distribution. With its intricate network of connectors, the motherboard orchestrates the symphony of hardware that makes computing possible.
Essential Power Connectors
ATX 24-pin Power Connector
At the heart of your motherboard's power delivery system lies the ATX 24-pin power connector. This robust connector is the primary power source for your motherboard and many of its components.
Typically located on the right edge of the motherboard, the 24-pin connector has evolved from its predecessor, the 20-pin connector. This transition was driven by the increasing power demands of modern components, ensuring that your system has sufficient electrical capacity to run smoothly.
When installing this connector, it's crucial to ensure it's fully seated. A partially connected ATX power connector can lead to system instability or failure to boot. You'll often hear a satisfying click when it's properly inserted.
8-pin EPS Connector
While the 24-pin connector powers most of the board, your CPU requires its own dedicated power source. This is where the 8-pin EPS (Extended Power Supply) connector comes into play.
Located near the top left corner of the motherboard, the EPS connector is specifically designed to provide stable, high-current power to the CPU. Some high-end motherboards may feature an additional 4-pin connector alongside the 8-pin, catering to extreme overclocking scenarios where power demands can skyrocket.
It's important to note that while EPS connectors may resemble PCIe power connectors, they are not interchangeable. Using the wrong connector can result in severe damage to your components, so always double-check before plugging in.
Storage Connectors
SATA Connectors
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) connectors have been the standard for connecting storage devices for over a decade. These L-shaped ports are usually found on the right side of the motherboard, often below the 24-pin connector.
Most modern motherboards feature between 4 to 6 SATA ports, allowing for multiple storage devices. SATA has gone through several revisions, with SATA III (6 Gbps) being the current standard for most systems.
While SATA remains widely used, especially for high-capacity hard drives, it's gradually being superseded by faster NVMe SSDs in high-performance systems. However, SATA's affordability and compatibility ensure its continued relevance in the near future.
M.2 Slots
M.2 slots represent the next generation of storage connectivity. These small, rectangular slots support both SATA and NVMe SSDs in the M.2 form factor. NVMe drives, in particular, offer significantly faster speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
When using M.2 slots, it's essential to consult your motherboard manual. Some M.2 slots may share bandwidth with certain SATA ports, potentially disabling them when an M.2 drive is installed. Understanding these interactions can prevent confusion during system setup.
USB Connectors
USB connectivity is a cornerstone of modern computing, and motherboards feature both external ports and internal connectors for front panel USB.
USB 3.0 Header
The USB 3.0 header, often found near the bottom right of the motherboard, is a large, rectangular 20-pin connector. It connects to your case's front panel USB 3.0 ports, providing high-speed USB access at the front of your system.
USB 2.0 Headers
USB 2.0 headers are smaller 9-pin connectors usually located along the bottom edge of the motherboard. While slower than USB 3.0, these headers are still useful for connecting front panel USB 2.0 ports and other internal USB devices like RGB controllers or internal card readers.
When connecting USB headers, precision is key. Never attempt to force USB 3.0 cables into USB 2.0 headers or vice versa, as this can damage your motherboard. Always refer to your motherboard manual for the correct orientation and location of these headers.
Fan and Cooling Connectors
Effective cooling is paramount for system stability and longevity. Modern motherboards offer various fan headers to accommodate different cooling solutions.
CPU Fan Connector
The CPU fan connector, located near the CPU socket, is critical for temperature management. Most motherboards won't boot without detecting a fan on this header, as it's a failsafe to prevent CPU damage from overheating.
System Fan Connectors
System fan connectors are distributed around the motherboard to power case fans. The number of these connectors varies, but mainstream boards typically offer 2 to 4. These headers allow for strategic placement of fans to optimize airflow within your case.
Water Pump Connector
For enthusiasts using liquid cooling, many modern motherboards include a dedicated water pump connector. This header often provides higher amperage than standard fan headers, catering to the power requirements of AIO or custom water cooling pumps.
Advanced motherboards may offer fan control through the BIOS or dedicated software, allowing users to create custom fan curves for optimal cooling and noise levels.
RGB and ARGB Connectors
The rise of PC aesthetics has led to the widespread adoption of RGB lighting in computer builds. Motherboards now commonly feature connectors for both standard RGB and addressable RGB (ARGB) devices.
RGB Headers
Standard RGB headers are 4-pin connectors that operate on 12V. These control basic RGB lighting where all LEDs in a strip or device change color simultaneously.
ARGB Headers
ARGB headers, in contrast, are 3-pin connectors operating at 5V. These allow for individual LED control, enabling more complex and dynamic lighting effects.
It's crucial to distinguish between these two types of headers, as connecting a 5V ARGB device to a 12V RGB header can result in damaged LEDs or other components.
Front Panel Connectors
The front panel connectors, while small, play a vital role in system functionality. These include:
- Power switch: Turns your PC on and off
- Reset switch: Restarts your system
- Power LED: Indicates when your PC is powered on
- HDD LED: Flashes to show drive activity
- Speaker: Provides beep codes for troubleshooting
Connecting these correctly requires careful attention to your motherboard manual, as the pinout can vary between manufacturers. While mixing these up won't cause permanent damage, it can lead to non-functional buttons or LEDs.
Audio Connector
The front panel audio connector, typically a block of 9 or 10 pins located in the bottom left corner of the motherboard, links to your case's front audio ports. While convenient, audiophiles often prefer using the rear audio ports connected directly to the motherboard for superior sound quality.
Specialized Connectors
TPM Header
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) header has gained prominence with the release of Windows 11. This connector allows for the installation of a TPM, which provides hardware-based security features. While not all users will need this, it's becoming increasingly important for future-proofing your system.
Thunderbolt Header
Some high-end motherboards feature a Thunderbolt header, allowing for the addition of Thunderbolt ports via an add-in card. Thunderbolt technology offers high-speed data transfer and versatile connectivity options, making it valuable for professionals working with large datasets or requiring fast external storage.
Troubleshooting Common Connector Issues
Even with careful assembly, issues can arise. Here are some common problems and their potential solutions:
PC Won't Turn On
- Verify that the 24-pin ATX connector is fully seated.
- Ensure the 8-pin EPS connector is properly connected.
- Double-check the front panel power switch connections.
- Consider using the motherboard's onboard power button (if available) to isolate case button issues.
USB Ports Not Working
- Confirm that the appropriate USB headers are connected correctly.
- Inspect USB headers for bent pins.
- Update motherboard chipset drivers.
- Check BIOS settings for any disabled USB controllers.
CPU Fan Error on Boot
- Ensure the CPU fan is connected to the designated CPU_FAN header.
- Verify that the fan is spinning.
- Check BIOS settings for fan speed thresholds.
No Video Output
- Confirm that the GPU is fully seated in its PCIe slot.
- Ensure all required GPU power connectors are connected.
- Try resetting the CMOS if all else fails.
- For systems with integrated graphics, ensure the display is connected to the motherboard's video output when troubleshooting.
Advanced Tips for Power Users
For enthusiasts looking to push their systems to the limit, consider these advanced techniques:
Multiple EPS Connectors: High-end motherboards often feature two 8-pin EPS connectors. For extreme overclocking scenarios, using both can provide more stable power delivery to the CPU.
Fan Curve Optimization: Delve into your motherboard's BIOS or provided software to create custom fan curves. This allows for a perfect balance between cooling performance and noise levels.
RGB Synchronization: If you're using RGB components from various manufacturers, consider using a unified software solution like OpenRGB. This can simplify the process of coordinating your system's lighting effects.
BIOS Flashback: Some motherboards offer a BIOS flashback feature, allowing for BIOS updates without a CPU installed. This can be invaluable when upgrading to a newer generation CPU that requires a BIOS update for compatibility.
Future-Proofing Your Build
When selecting a motherboard, consider these factors for future expandability:
PCIe Lanes: More PCIe lanes allow for additional expansion cards and NVMe drives. This is especially important for users who plan to use multiple high-speed storage devices or GPUs.
USB Headers: Look for motherboards with USB 3.2 Gen 2 and USB-C headers. These will support faster future peripherals and maintain relevance as USB standards evolve.
RAM Slots: Opting for a motherboard with four RAM slots instead of two provides an easier upgrade path, allowing you to add more memory without replacing existing modules.
VRM Quality: For those interested in overclocking or using high-performance CPUs, a robust VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) design is crucial. This ensures stable power delivery even under heavy loads.
The Future of Motherboard Connectors
As technology advances, we can expect to see evolution in motherboard connectors. Some trends to watch for include:
Increased Adoption of USB4: This will likely lead to new header designs on motherboards to support higher speeds and power delivery.
PCIe 5.0 and Beyond: As PCIe standards advance, we may see changes in connector design to support increased bandwidth requirements.
Wireless Charging Integration: Some high-end motherboards are beginning to incorporate Qi wireless charging. This trend may continue, leading to new types of power-related connectors.
AI-Assisted Overclocking: As AI becomes more prevalent in computing, we might see new connectors or headers designed to support dedicated AI processing units for tasks like real-time system optimization.
Conclusion
Understanding motherboard connectors is crucial for building, maintaining, and troubleshooting your PC. Each connector plays a vital role in bringing your system to life, from delivering power to facilitating high-speed data transfer. As you embark on your next build or upgrade, remember that patience and careful attention to detail are your best allies.
The world of PC hardware is ever-evolving, with new standards and technologies constantly emerging. Staying informed about these changes will help you make educated decisions when selecting components and troubleshooting issues. Whether you're a casual user or a hardcore enthusiast, I hope this guide has deepened your understanding of motherboard connectors and inspired you to explore the intricacies of PC building.
Remember, every great system starts with a solid foundation, and that foundation is built on the correct usage of these essential connectors. Happy building, and may your systems always post on the first try!